Article Text
Abstract
Background Hypospadias surgery has been continuously evolving, although there is no single technique which can be said to be perfect and suitable for all types of hypospadias. Tubularized incised plate (TIP) urethroplasty (Snodgrass procedure) is presently the most common surgical procedure performed for distal penile hypospadias (DPH). The aim of this study was to compare the outcome of TIP urethroplasty using Dartos flap (DF) and spongioplasty as second layer in DPH.
Methods A total of 30 patients of DPH were repaired using TIP urethroplasty with DF or spongioplasty as second layer from January 2017 to June 2018. Out of 30 patients, TIP with DF was done in 15 patients (group A) and TIP with spongioplasty was done in the remaining 15 patients (group B). Preoperative mean age and weight were comparable in both groups. Postoperative complications, namely, postoperative edema, residual chordee, urethrocutaneous fistula (UCF), meatal stenosis and final cosmesis, were recorded.
Results In both groups, complications included postoperative edema (Gp A-1Gp B-1), residual chordee (Gp A-1, Gp B-1), UCF (Gp A-3, Gp B-4), meatal stenosis (Gp A-1, Gp B-5) and poor cosmesis (Gp A-3, Gp B-4). Wound infection was managed with appropriate antibiotics, and meatal stenosis responded to calibration in five patients.
Although it seems that DF has a better outcome clinically, the difference between the two techniques was statistically not significant.
Conclusion DF as an additional cover to TIP is associated with an acceptable complication and has good cosmesis compared with spongioplasty; however, the difference is not statistically significant.
- pediatrics
Data availability statement
Data are available on reasonable request. All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information. All the relevant data related to the study have been included in the article, although if needed, raw data will be made available.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Key messages
What is already known about this subject?
Hypospadias is a common congenital anomaly seen in the male child with no universally acceptable technique for repair.
The Snodgrass tubularized incised plate (TIP) urethroplasty has become a primary technique for repair of distal and middle hypospadias.
Interposing vascularized flaps between neourethra and skin sutures is recommended to decrease the rate of urethrocutaneous fistula.
What are the new findings?
This study compared outcomes of Dartos flap (DF) and spongioplasty as second layer in Snodgrass repair in distal penile hypospadias.
The study showed that DF coverage of the neourethra after TIP urethroplasty had less complication compared with spongioplasty cover, although the result was not statistically significant.
How might it impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
Both DF and spongioplasty can be used as second layer with few complications although the use of corpus spongiosum alone to cover the neourethra is infrequent.
Findings of our study may encourage other authorities to compare these techniques in a large number of patients and can support our result.
Introduction
Hypospadias is a common congenital anomaly seen in the male child having abnormal position of the external urethral meatus. Hypospadias is associated with downward curvature of the penis or dorsal hood in some cases which potentially impacts both urinary and sexual function. Modern surgical correction most often involves tubularization of the urethral plate, which normally should have completed urethral development.1 The goals of hypospadias surgery are to correct the penile curvature, to reconstruct a forward directed urinary stream and to achieve good cosmesis.
There is no single, universally acceptable technique for hypospadias repair. Command of a technically straightforward repair with few complications and with proven success and versatility in a reasonable range of hypospadias defects are desired goals of hypospadias surgery. The Snodgrass tubularized incised plate (TIP) urethroplasty has become a primary technique for repair of distal and middle hypospadias.2 Although many techniques have been introduced for the treatment of hypospadias, urethrocutaneous fistula (UCF) and meatal stenosis, which are the most frequent complications requiring reoperation, may develop even in the hands of experienced surgeons. Interposing vascularized flaps between neourethra and skin sutures is recommended in hypospadias surgery to decrease the rate of UCF. Flaps commonly used are de-epithelialized skin,3 4 corpus spongiosum,5 tunica vaginalis flap6–8 and dartos fascia9; however, the flap which provides a better cover is still a matter of controversy because results have been conflicting and differing in the hands of different surgeons.
The aim of the present study is to present our experience with reinforcing Dartos flap (DF) and spongioplasty to TIP urethroplasty in distal penile hypospadias (DPH).
Methods
A prospective study was conducted between January 2017 and June 2018 in the Department of Pediatric Surgery, Atal Bihari Vajpayee Institute of Medical Sciences and Dr Ram Manohar Lohia Hospital, New Delhi.
The study population consisted of 30 patients with primary DPH. Children <12 years undergoing primary repair were included in the study after proper informed consent from the patient’s guardian.
Previously operated cases and cases with other genitourinary anomaly, such as undescended testes or hernia, were excluded from the study. All patients were operated under general anaesthesia because this is the most suitable mode for children.
Out of 30 patients, TIP with DF was done in 15 patients (group A) and the remaining 15 patients received TIP with spongioplasty (group B). Patients were randomly assigned to group A or group B. Postoperative complications, such as postoperative edema, residual chordee, UCF, meatal stenosis, and final appearance or cosmesis (as per parents’ satisfaction), were recorded. All patients were followed at 2 weeks, 1 month and 3 months after discharge with mean postoperative follow-up of 6 months. The collected data were analyzed and statistically evaluated using SPSS-PC V.17. Difference between proportions was tested by χ2test and p value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Re-do surgery and other intervention as fistula closure were considered as a failure of the operative procedure. All cases were done by single senior surgeon in the department.
Surgical technique
In both groups, the general technique was the same as described by Snodgrass.10 Fine instruments and bipolar electrocautery were used. A U-shaped incision was made encircling the meatus up to the corona, preserving the urethral plate and then extended circumferentially around the corona to complete the degloving. Gitte’s test was done to evaluate the chordee after penile degloving. Incised urethral plate was tubularized over an appropriately sized catheter using 6-0 polyglactin suture.
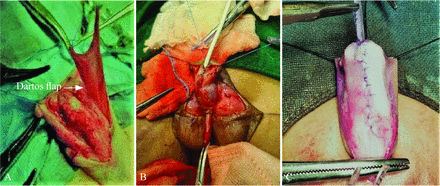
The technique of putting a soft-tissue cover over this neourethra differed in both the groups. In group A, the dartos was used as cover for the suture line, which was harvested from the dorsal prepuce and the penile skin, with meticulous dissection (figure 1A). The dartos fascia was placed ventrally over the neourethra and sutured with 6-0 polyglactin sutures.
Surgical technique of Dartos flap and spongioplasty in Snodgrass urethroplasty. (A) Dartos flap raised between penile skin and dorsal dartos; (B) spongioplasty being done; (C) spongioplasty completed.
In group B, corpous spongiosum was used as second cover over neourethra. Sometimes it may not be possible to get enough spongiosum, but fortunately we got satisfactory spongiosum in all patients randomized to this group. Started from proximal to the hypospadiac meatal opening, proper plane was created between Buck’s fascia and tunica albuginea and the dissection was carried out on the penile shaft lateral to the margin of the corpus spongiosum. From lateral to medial, the spongiosum was dissected off the underlying corpora cavernosa.11 Dissection was performed meticulously to avoid damage to the corpus spongiosum or corpus cavernosum. The mobilized spongiosum from both sides were then approximated in the midline with 6-0 polyglactin suture in continuous manner to cover the entire neourethra (figure 1B,C).
Light compression dressing was applied. Intravenous antibiotics were given for 5 days, followed by oral antibiotics. Dressing was opened on postoperative day 4 or 5, and urethral stent was removed on the 10th day.
Results
The study included 30 patients with DPH. Fifteen patients were repaired using DF (group A) and the remaining 15 patients using spongioplasty (group B) as flap over TIP urethroplasty. The mean age and weight of the patients in both groups was comparable. In group A, mean age and weight were 6.14 years and 14.43 kg, respectively, and in group B mean age and weight were 5.88 years and 14.88 kg, respectively.
Morphological data of each patient, including type of hypospadias, glans type, urethral plate size and pre-operative chordee, were recorded (table 1).
Morphological data of patients in both groups
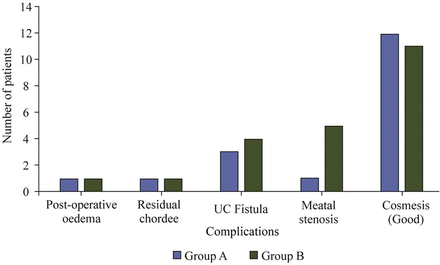
Preoperatively, chordee was present in 7 cases (4 in group A, 3 in group B). In group A, 2 patients had chordee of more than 40 degrees, which was corrected by degloving followed by dorsi plication to minimize the chordee. In group A, 4/15 (26.67%) had preop chordee, 1/15 (6.67%) had postoperative edema, 1/15 (6.67%) had residual chordee, 3/15 (20%) had UCF, 1/15 (6.67%) had meatal stenosis and 3/15 (20%) had poor cosmesis. In group B, 3/15 (20%) had preop chordee, 1/15 (6.67%) had postoperative edema, 1/15 (6.67%) had residual chordee, 4/15 (26.67%) had UCF, 5/15 (33.33%) had meatal stenosis and 4/15 (26.67%) had poor cosmesis (table 2 and figure 2).
Correlation of flap and their complications
Bar diagram showing different complications in both groups (group A—tubularized incised plate+Dartos flap, group B—tubularized incised plate+spongioplasty). UC, urethrocutaneous.
The patients’ wound infection was managed with appropriate antibiotics, and 5 out of 6 patients had meatal stenosis responded to calibration during follow-up period. All patients with fistula were successfully repaired with fistula closure without need to redo urethroplasty. None of the patients had stricture of the urethra, and residual chordee was in acceptable range (10–15 degrees).
Given these results, DF repair appears to be better than spongioplasty, but there is actually no statistically significant difference between the two techniques in terms of prevention of UCF, in terms of cosmesis and other complications except meatal stenosis, although it is not related to type of flap.
Discussion
TIP urethroplasty for hypospadias has gained widespread acceptance due to its versatility, lower complication rate and reliable creation of vertically oriented meatus, with excellent cosmesis.12 13 The use of a waterproofing second cover for the neourethra is well documented in the literature varying from dartos-based flaps (ventral, dorsal and scrotal dartos flaps), TV flap, to corpus spongiosum, which is known to decrease the incidence of UCF.14–24 Despite obvious surgical advances in hypospadias repair, no single technique has been free of complication.18 The common complications reported after TIP urethroplasty repair include fistula, urethral stricture, meatal stenosis and persistent chordee. UCF is the most common complication, and the causes of fistula may be local infection, ischemia and distal obstruction due to meatal stenosis.25
The use of spongiosal tissue as an intermediate layer between the urethra and skin was described in 2000 by Yerkes and Beaudoin in two different studies.5 11 26 Yerkes reported no UCF in the patients with spongioplasty used as second layer after TIP repair, whereas Beaudoin described the anatomical characteristics of the spongiosal layer in the hypospadiac penis and implemented spongioplasty in patients with hypospadias.11
The reported fistula rate with spongioplasty ranges from 0% to 31%,14 which is comparable with our result (ie, 26.7%). Bhat et al have shown a very low fistula rate with spongioplasty after Snodgrass repair.15 Several investigators have shown spongioplasty to be as protective as a DF, but others have found spongioplasty to be associated with high fistula rates compared with standard DF.27 Spongiosal tissue is not always well developed or available and may not be mobilized over the neourethral suture line.
DF is a layer of connective tissue found in the penile dorsal or ventral area, foreskin and scrotum, and can be used in hypospadias or fistula repair in different techniques.28 29 Excellent vascularity, easy availability and adequate source are advantages of DF, making this flap technique more popular, especially among young surgeons. Preputial skin necrosis and penile rotation are commonly reported complications with the DF, but they can be avoided by careful operation and technical improvement. Smith performed TIP urethroplasty with ventral based dartos pedicle flap for covering the neourethra in 56 patients without complication.17 While Furness reported that of the 111 patients with reconstruction using the ventral based dartos pedicle flap to cover the TIP, urethroplasty was successful in 109 (98.2%) with only 2 patients developing UCF.18 We found 80% of cases without complication in DF group. Dartos-based flaps have the advantage of being available locally and do not require another incision or extension of the incision. Soygur et al adopted the ventral based DF and found the flap much easier to construct with little time added to surgery and no harvesting-related complications.19 They also obtained satisfactory results with a fistula rate of 8.3%. Hayashi et al reported an incidence of 9% fistula rate with ventral based dartos flap.20
We could not find any article comparing these two methods of soft-tissue cover in English literature. The main limitation of our study was that the number of patients was not quite large. Hypospadias surgery is a technically challenging procedure, and different results can be obtained in different hands with different experience.
In conclusion, intervening flap covering urethral tube should be the part of the Snodgrass procedure. A dorsal well‐vascularized DF is a good choice for preventing fistula. Redundancy of the flap and its excellent vascularization depends on the harvesting technique.
We found that DF coverage of the neourethra after TIP urethroplasty had less complication compared with spongioplasty cover, although the result was not statistically significant. However, spongioplasty can be used as an additional cover because it provides well-vascularized, spongy protective covering to the neourethra and it also reduces the degree of penile curvature and can be helpful in avoiding dorsal plication in some of the patients with hypospadias with moderately severe curvature.
Data availability statement
Data are available on reasonable request. All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information. All the relevant data related to the study have been included in the article, although if needed, raw data will be made available.
Ethics statements
Ethics approval
This study was approved by Institutional ethics committee, PGIMER, Dr Ram Manohar Lohia Hospital, Delhi with reference no. F. No. TP(DM/M.Ch) (10/2016)/IEC/PGIMER/RMLH 7964/16.
References
Footnotes
Contributors AV contributed to conceptualization, formal analysis, data curation and writing – original draft. SM cpntributed to data curation and methodology. VKK cotributed to conceptualization, supervision and writing- review and editing. AS contributed to conceptualization, supervision and writing- review and editing. DG contributed to data curation. All the authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.