Abstract
Purpose
The proto-oncogene beta-catenin is linked to an abnormal activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin-pathway and shows mutations in 50–90 % of hepatoblastoma (HB). Corresponding, the recently published murine orthotopic HB model differs from the former subcutaneous model by nuclear beta-catenin distribution. As the nuclear localization of beta-catenin is considered to reflect a more aggressive tumor growth, the influence of beta-catenin inhibition on cell viability and drug-efficiency in HB cells was analyzed.
Methods
Beta-catenin distribution in HB cells was analyzed by immunofluorescence. The influence of beta-catenin inhibitors Celecoxib, Etodolac, ICG001, and MET kinase inhibitor (SU11274) alone and in combination with cisplatin (CDDP) on HB cell lines (HuH6, HepT1) was evaluated by cell viability assays and BrdU incorporation.
Results
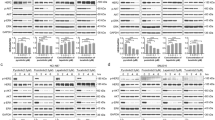
Celecoxib and ICG001 reduced dose-dependently HB cell viability and decreased nuclear beta-catenin in cultivated HB cells. Etodolac was without influence at concentrations up to 100 μM. Combinations of Celecoxib or ICG001 with MET kinase inhibitor or CDDP resulted in additive reduction of cell viability.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical beta-catenin inhibitors can modulate the nuclear localization of beta-catenin and reduce cell viability of HB cells in vitro. These promising effects might optimize the outcome of high-risk HB. The orthotopic HB model is a suitable basis for further in vivo studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zsiros J, Maibach R, Shafford E, Brugieres L, Brock P, Czauderna P, Roebuck D, Childs M, Zimmermann A, Laithier V, Otte JB, de Camargo B, MacKinlay G, Scopinaro M, Aronson D, Plaschkes J, Perilongo G (2010) Successful treatment of childhood high-risk hepatoblastoma with dose-intensive multiagent chemotherapy and surgery: final results of the SIOPEL-3HR study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 28(15):2584–2590. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.22.4857
Zimmermann A (2005) The emerging family of hepatoblastoma tumours: from ontogenesis to oncogenesis. Eur J Cancer 41(11):1503–1514. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2005.02.035
Honda S, Arai Y, Haruta M, Sasaki F, Ohira M, Yamaoka H, Horie H, Nakagawara A, Hiyama E, Todo S, Kaneko Y (2008) Loss of imprinting of IGF2 correlates with hypermethylation of the H19 differentially methylated region in hepatoblastoma. Br J Cancer 99(11):1891–1899. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604754
Rainier S, Dobry CJ, Feinberg AP (1995) Loss of imprinting in hepatoblastoma. Cancer Res 55(9):1836–1838
Lopez-Terrada D, Gunaratne PH, Adesina AM, Pulliam J, Hoang DM, Nguyen Y, Mistretta TA, Margolin J, Finegold MJ (2009) Histologic subtypes of hepatoblastoma are characterized by differential canonical Wnt and notch pathway activation in DLK + precursors. Hum Pathol 40(6):783–794. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2008.07.022
Koch A, Denkhaus D, Albrecht S, Leuschner I, von Schweinitz D, Pietsch T (1999) Childhood hepatoblastomas frequently carry a mutated degradation targeting box of the beta-catenin gene. Cancer Res 59(2):269–273
Koch A, Waha A, Hartmann W, Hrychyk A, Schuller U, Waha A, Wharton KA Jr, Fuchs SY, von Schweinitz D, Pietsch T (2005) Elevated expression of Wnt antagonists is a common event in hepatoblastomas. Clin cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 11(12):4295–4304. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1162
Wei Y, Fabre M, Branchereau S, Gauthier F, Perilongo G, Buendia MA (2000) Activation of beta-catenin in epithelial and mesenchymal hepatoblastomas. Oncogene 19(4):498–504. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203356
Yamaoka H, Ohtsu K, Sueda T, Yokoyama T, Hiyama E (2006) Diagnostic and prognostic impact of beta-catenin alterations in pediatric liver tumors. Oncol Rep 15(3):551–556
Purcell R, Childs M, Maibach R, Miles C, Turner C, Zimmermann A, Sullivan M (2011) HGF/c-Met related activation of beta-catenin in hepatoblastoma. J Exp Clini Cancer Res CR 30:96. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-30-96
Park WS, Oh RR, Park JY, Kim PJ, Shin MS, Lee JH, Kim HS, Lee SH, Kim SY, Park YG, An WG, Jang JJ, Yoo NJ, Lee JY (2001) Nuclear localization of beta-catenin is an important prognostic factor in hepatoblastoma. J Pathol 193(4):483–490
Gavert N, Ben-Ze’ev A (2007) Beta-catenin signaling in biological control and cancer. J Cell Biochem 102(4):820–828. doi:10.1002/jcb.21505
Klaus A, Birchmeier W (2008) Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8(5):387–398. doi:10.1038/nrc2389
Ellerkamp V, Armeanu-Ebinger S, Wenz J, Warmann SW, Schafer J, Ruck P, Fuchs J (2011) Successful establishment of an orthotopic hepatoblastoma in vivo model in NOD/LtSz-scid IL2Rgammanull mice. PLoS ONE 6(8):e23419. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023419
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X (2009) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 17(1):9–26. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.016
Monga SP, Mars WM, Pediaditakis P, Bell A, Mule K, Bowen WC, Wang X, Zarnegar R, Michalopoulos GK (2002) Hepatocyte growth factor induces Wnt-independent nuclear translocation of beta-catenin after Met-beta-catenin dissociation in hepatocytes. Cancer Res 62(7):2064–2071
Pietsch T, Fonatsch C, Albrecht S, Maschek H, Wolf HK, von Schweinitz D (1996) Characterization of the continuous cell line HepT1 derived from a human hepatoblastoma. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol 74(4):809–818
Doi I (1976) Establishment of a cell line and its clonal sublines from a patient with hepatoblastoma. Gann = Gan 67(1):1–10
Lieber J, Kirchner B, Eicher C, Warmann SW, Seitz G, Fuchs J, Armeanu-Ebinger S (2010) Inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-X enhances chemotherapy sensitivity in hepatoblastoma cells. Pediatr Blood Cancer 55(6):1089–1095. doi:10.1002/pbc.22740
Dewerth A, Wonner T, Lieber J, Ellerkamp V, Warmann SW, Fuchs J, Armeanu-Ebinger S (2012) In vitro evaluation of the Aurora kinase inhibitor VX-680 for Hepatoblastoma. Pediatr Surg Int 28(6):579–589. doi:10.1007/s00383-012-3086-6
Oue T, Yoneda A, Uehara S, Yamanaka H, Fukuzawa M (2009) Increased expression of multidrug resistance-associated genes after chemotherapy in pediatric solid malignancies. J Pediatr Surg 44(2):377–380. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2008.10.088
Warmann S, Hunger M, Teichmann B, Flemming P, Gratz KF, Fuchs J (2002) The role of the MDR1 gene in the development of multidrug resistance in human hepatoblastoma: clinical course and in vivo model. Cancer 95(8):1795–1801. doi:10.1002/cncr.10858
Sawyers C (2004) Targeted cancer therapy. Nature 432(7015):294–297. doi:10.1038/nature03095
He B, You L, Uematsu K, Xu Z, Lee AY, Matsangou M, McCormick F, Jablons DM (2004) A monoclonal antibody against Wnt-1 induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Neoplasia 6(1):7–14
Lee JS, Hur MW, Lee SK, Choi WI, Kwon YG, Yun CO (2012) A novel sLRP6E1E2 inhibits canonical Wnt signaling, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in lung cancer. PLoS ONE 7(5):e36520. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036520
Purcell R, Childs M, Maibach R, Miles C, Turner C, Zimmermann A, Czauderna P, Sullivan M (2011) Potential biomarkers for hepatoblastoma: results from the SIOPEL-3 study. Eur J Cancer. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.10.019
Ueda Y, Hiyama E, Kamimatsuse A, Kamei N, Ogura K, Sueda T (2011) Wnt signaling and telomerase activation of hepatoblastoma: correlation with chemosensitivity and surgical resectability. J Pediatr Surg 46(12):2221–2227. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2011.09.003
Curtin JC, Lorenzi MV (2010) Drug discovery approaches to target Wnt signaling in cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 1(7):563–577
Herencia C, Martinez-Moreno JM, Herrera C, Corrales F, Santiago-Mora R, Espejo I, Barco M, Almaden Y, de la Mata M, Rodriguez-Ariza A, Munoz-Castaneda JR (2012) Nuclear translocation of beta-catenin during mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into hepatocytes is associated with a tumoral phenotype. PLoS ONE 7(4):e34656. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034656
Zulehner G, Mikula M, Schneller D, van Zijl F, Huber H, Sieghart W, Grasl-Kraupp B, Waldhor T, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Beug H, Mikulits W (2010) Nuclear beta-catenin induces an early liver progenitor phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumor recurrence. Am J Pathol 176(1):472–481. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090300
Curia MC, Zuckermann M, De Lellis L, Catalano T, Lattanzio R, Aceto G, Veschi S, Cama A, Otte JB, Piantelli M, Mariani-Costantini R, Cetta F, Battista P (2008) Sporadic childhood hepatoblastomas show activation of beta-catenin, mismatch repair defects and p53 mutations. Mod Pathol Off J US Can Acad Pathol Inc 21(1):7–14. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800977
Ranganathan S, Tan X, Monga SP (2005) Beta-catenin and met deregulation in childhood Hepatoblastomas. Pediatr Dev Pathol Off J Soc Pediatr Pathol Paediatr Patholo Soc 8(4):435–447. doi:10.1007/s10024-005-0028-5
Gupta K, Rane S, Das A, Marwaha RK, Menon P, Rao K (2012) Relationship of beta-catenin and postchemotherapy histopathologic changes with overall survival in patients with hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. doi:10.1097/MPH.0b013e3182580471
Park SE, Yoo HS, Jin CY, Hong SH, Lee YW, Kim BW, Lee SH, Kim WJ, Cho CK, Choi YH (2009) Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of telomerase activity in human lung carcinoma cells by the water extract of Cordyceps militaris. Food Chem Toxicol Int J Publ Br Ind Biol Res Assoc 47(7):1667–1675. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.04.014
Shalaby T, Hiyama E, Grotzer MA (2010) Telomere maintenance as therapeutic target in embryonal tumours. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 10(3):196–212
Thun MJ, Henley SJ, Patrono C (2002) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as anticancer agents: mechanistic, pharmacologic, and clinical issues. J Natl Cancer Inst 94(4):252–266
Greenspan EJ, Madigan JP, Boardman LA, Rosenberg DW (2011) Ibuprofen inhibits activation of nuclear {beta}-catenin in human colon adenomas and induces the phosphorylation of GSK-3{beta}. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 4(1):161–171. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0021
Eberhart CE, Coffey RJ, Radhika A, Giardiello FM, Ferrenbach S, DuBois RN (1994) Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 gene expression in human colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology 107(4):1183–1188
Grosch S, Maier TJ, Schiffmann S, Geisslinger G (2006) Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-independent anticarcinogenic effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(11):736–747. doi:10.1093/jnci/djj206
Behari J, Zeng G, Otruba W, Thompson MD, Muller P, Micsenyi A, Sekhon SS, Leoni L, Monga SP (2007) R-Etodolac decreases beta-catenin levels along with survival and proliferation of hepatoma cells. J Hepatol 46(5):849–857. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2006.11.017
Yao H, Ashihara E, Maekawa T (2011) Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human cancers. Expert Opin Ther Targ 15(7):873–887. doi:10.1517/14728222.2011.577418
Tuynman JB, Vermeulen L, Boon EM, Kemper K, Zwinderman AH, Peppelenbosch MP, Richel DJ (2008) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition inhibits c-Met kinase activity and Wnt activity in colon cancer. Cancer Res 68(4):1213–1220. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5172
Andre N, Abed S, Orbach D, Alla CA, Padovani L, Pasquier E, Gentet JC, Verschuur A (2011) Pilot study of a pediatric metronomic 4-drug regimen. Oncotarget 2(12):960–965
Buendia MA (2002) Genetic alterations in hepatoblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma: common and distinctive aspects. Med Pediatr Oncol 39(5):530–535. doi:10.1002/mpo.10180
Emami KH, Nguyen C, Ma H, Kim DH, Jeong KW, Eguchi M, Moon RT, Teo JL, Kim HY, Moon SH, Ha JR, Kahn M (2004) A small molecule inhibitor of beta-catenin/CREB-binding protein transcription [corrected]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(34):12682–12687. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404875101
Henderson WR Jr, Chi EY, Ye X, Nguyen C, Tien YT, Zhou B, Borok Z, Knight DA, Kahn M (2010) Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin/CREB binding protein (CBP) signaling reverses pulmonary fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(32):14309–14314. doi:10.1073/pnas.1001520107
Goodman RH, Smolik S (2000) CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation, and development. Genes Dev 14(13):1553–1577
Gao J, Inagaki Y, Song P, Qu X, Kokudo N, Tang W (2012) Targeting c-Met as a promising strategy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol Res Off J Italian Pharmacol Soc 65(1):23–30. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2011.11.011
Lieber J, Ellerkamp V, Wenz J, Kirchner B, Warmann SW, Fuchs J, Armeanu-Ebinger S (2012) Apoptosis sensitizers enhance cytotoxicity in hepatoblastoma cells. Pediatr Surg Int 28(2):149–159. doi:10.1007/s00383-011-2988-z
Yallapu MM, Maher DM, Sundram V, Bell MC, Jaggi M, Chauhan SC (2010) Curcumin induces chemo/radio-sensitization in ovarian cancer cells and curcumin nanoparticles inhibit ovarian cancer cell growth. J Ovarian Res 3:11. doi:10.1186/1757-2215-3-11
Wang J, Zhou D, He X, Wang Y, Hu W, Jiang L, Dou J (2011) Effect of downregulated beta-catenin on cell proliferative activity, the sensitivity to chemotherapy drug and tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol 57(Suppl):OL1606–OL1613
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellerkamp, V., Lieber, J., Nagel, C. et al. Pharmacological inhibition of beta-catenin in hepatoblastoma cells. Pediatr Surg Int 29, 141–149 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-012-3237-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-012-3237-9